Most Used Functions in Excel
Functions in Excel make your calculation a lot easier. In this lesson, we are going to show the ten most widely used functions in Excel- COUNT, SUM, AVERAGE, IF, COUNTIF, SUMIF, VLOOKUP, MIN, MAX, and SUMPRODUCT.
1. COUNT
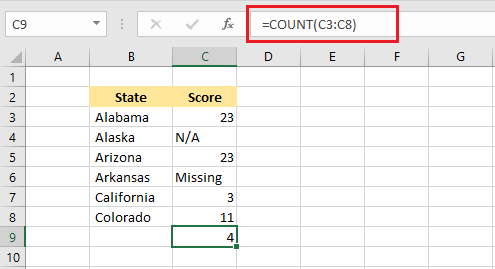
COUNT function in Excel counts the number of cells containing numeric values.
2. SUM
SUM function in Excel adds all values in a range of cells.
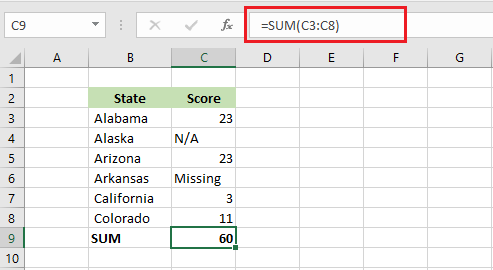
Note: Excel ignores cells with character values while executing SUM.
3. AVERAGE
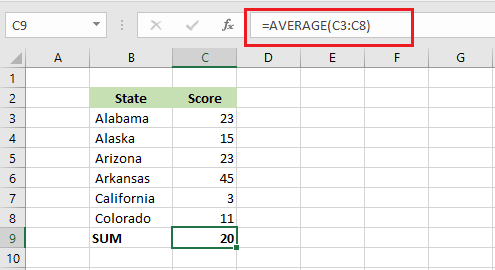
AVERAGE function in Excel calculates the arithmetic mean (aka. simple mean/equally weighted mean) of values in a range of cells.
4. IF
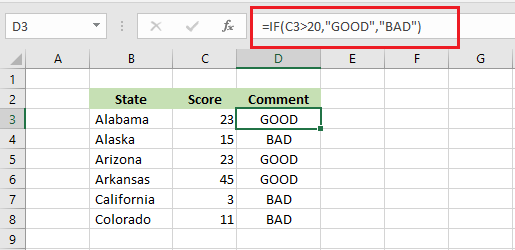
IF function in Excel is a conditional function. It returns a value or performs an action if TRUE and returns or performs another action if FALSE.
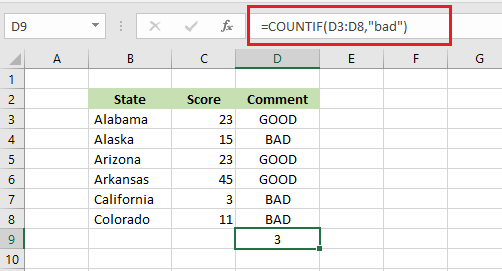
5. COUNTIF
COUNTIF function in Excel counts with a condition. For instance, the example below counts how many cells have “BAD” in them.
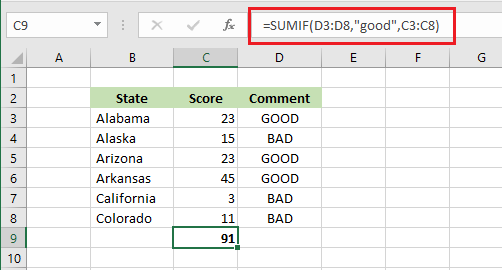
6. SUMIF
SUMIF function in Excel is also a conditional function that sums the values in cells when some conditions are met. For instance, the example below adds the values in cells that have “good” in them.
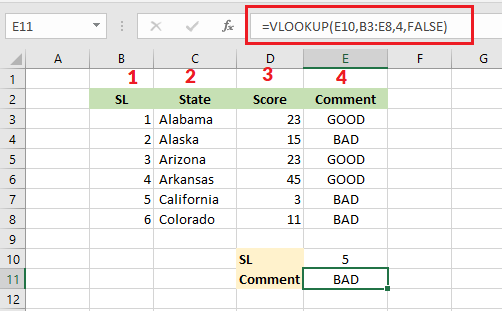
7. VLOOKUP
In the example below, the VLOOKUP function finds the comment for the state that has a serial number of 5. Here is the breakdown. First, Excel takes the value 5 (E10) to find a match in the left-most column (column B). Second, it identifies imaginary columns (1, 2, 3, 4) in your defined range (B3:E8). Third, when it finds a match of SL 5, the function returns “BAD” from the comment column (4).
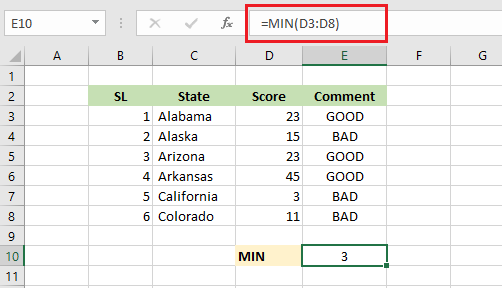
8. MIN
The MIN function in Excel returns the minimum value from a series of numbers.
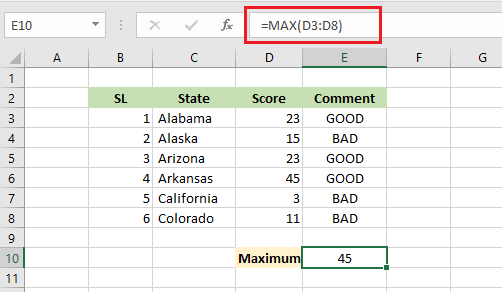
9. MAX
The MAX function in Excel returns the maximum value from a series of numbers.
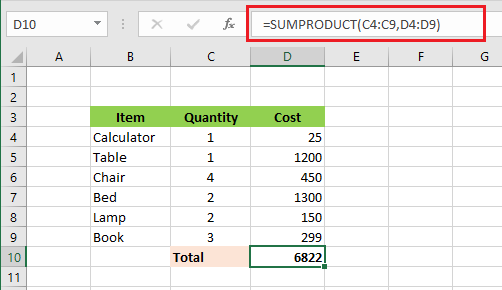
10. SUMPRODUCT
The SUMPRODUCT function in Excel calculates the sum of products of cells in the range. The example below calculates the total cost in cell D10 by multiplying columns C and D and then adding those up. Specifically, 6822 = (1*25) + (1*1200) + (4*450) + (2*1300) + (2*150) + (3*299).
| 2 of 10 finished! Recommending more on Formulas and Functions: Next Example >> |
| << Previous Example | Skip to Next Chapter 07: Find and Select |
